Study clarifies how physical exercise burns muscle fat
An article published in Science Advances describes for the first time a neuromuscular circuit that links the burning of muscle fat to the action of a protein in the brain.
The findings, obtained in Brazil by researchers at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP) and the University of São Paulo (USP), contribute to a deeper understanding of how regular physical exercise helps weight loss, reinforcing the importance of this habit to good health.
“We set out to study the action of a protein called interleukin 6 [IL-6], which is a pro-inflammatory cytokine but performs different functions in some situations including exercise. In this case, the function is burning muscle fat,” said Eduardo Ropelle, last author of the article. Ropelle is a professor at UNICAMP’s School of Applied Sciences (FCA) in Limeira and is supported by FAPESP.
The group led by Ropelle had already observed in mice that muscle fat oxidation began immediately in the legs when the protein was injected directly into the brain. This part of the study was conducted during the master’s research of Thayana Micheletti. She performed part of the analysis during a research internship at the University of Santiago de Compostela in Spain.
The researchers analyzed the results to find out whether there was a neural circuit linking production of IL-6 in the hypothalamus, a brain region that controls several functions, to the breakdown of skeletal muscle fat. This part of the study was conducted with the collaboration of Carlos Katashima, who is currently on a postdoctoral internship at FCA-UNICAMP’s Laboratory of Molecular Biology of Exercise (LaBMEx), headed by Ropelle.
Previous studies showed that a specific part of the hypothalamus (the ventromedial nucleus) could alter muscle metabolism when stimulated. On detecting the presence of IL-6 receptors in this brain region, Brazilian researchers formulated the hypothesis that the protein produced there might activate a neuromuscular circuit that favored the burning of skeletal muscle fat.
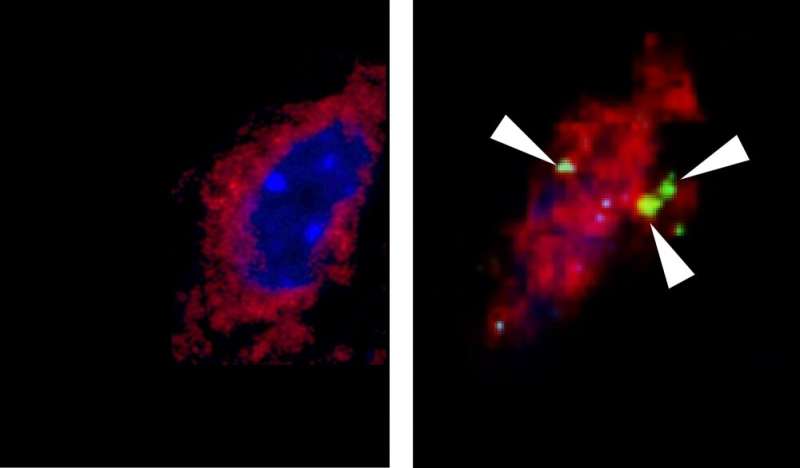
Several experiments were performed to demonstrate the circuit’s existence. In one, Katashima and colleagues excised part of the sciatic nerve in one of the legs of each mouse. The sciatic nerve runs from the lower spine to the feet.
When IL-6 was injected into the brain, fat was burned as expected in the intact legs but not in the leg with the severed nerve. “The experiment showed that muscle fat is metabolized only thanks to the nervous connection between hypothalamus and muscle,” Katashima said.
Blocked receptors
To find out how the nervous system was linked to the muscles, the researchers administered drugs that blocked the mice’s alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors, in this case responsible for receiving nervous signals for muscles to perform the function determined by the brain.
Blocking beta-adrenergic receptors had little effect, but muscle fat oxidation stopped or was sharply reduced when alpha-adrenergic receptors were blocked.
Computer simulations (in silico analysis) showed hypothalamic IL-6 gene expression to be strongly correlated with two muscle alpha-adrenergic receptor subunits (adrenoreceptors alpha2A and alpha2C). When IL-6 was injected into the brains of mice genetically engineered not to produce these receptors, the results were validated: leg muscle fat was not metabolized in these mice.
“An important finding of the study was the association between this neuromuscular circuit and afterburn, which is fat oxidation that occurs after exercise has ceased. This has been considered secondary, but in fact, it can last for hours and should be considered vitally important to the process of weight loss,” Ropelle said.
Source: Read Full Article