Use of immunosuppressants for inflammatory rheumatic diseases and the associated risk of severe COVID-19
A recent study posted to the medRxiv* preprint server investigated the risk of severe/fatal coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in patients treated with immunosuppressants for inflammatory rheumatic diseases (IRD).
Since the early COVID-19 phase in the United Kingdom (UK), people on immunosuppressive therapies were considered highly susceptible to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and advised to exercise caution and shield themselves. Subsequently, as COVID-19 vaccines became available, these people were eligible for high-priority primary vaccination.
Study: Risk of severe COVID-19 in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases treated with immunosuppressive therapy in Scotland. Image Credit: NIAID
The study
In the present study, researchers assessed the association of severe or fatal COVID-19 with IRD and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Data of patients receiving immunosuppressants were requested from clinicians, and the lists of such patients were obtained from National Health Service (NHS) Grampian, NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde, and NHS Lothian.
These patients' lists were merged into one and linked with the Rapid Epidemiological Analysis of Comorbidities and Treatments as risk factors for COVID-19 in Scotland (REACT-SCOT) study. This case-control study included all COVID-19 cases in Scotland and over three million people as controls. The dataset of the REACT-SCOT research is linked to the national database containing information on vaccinations, outpatient consultations, and hospital discharges from the last five years, primary care prescription data from the previous 240 days, and a list of patients to be shielded.
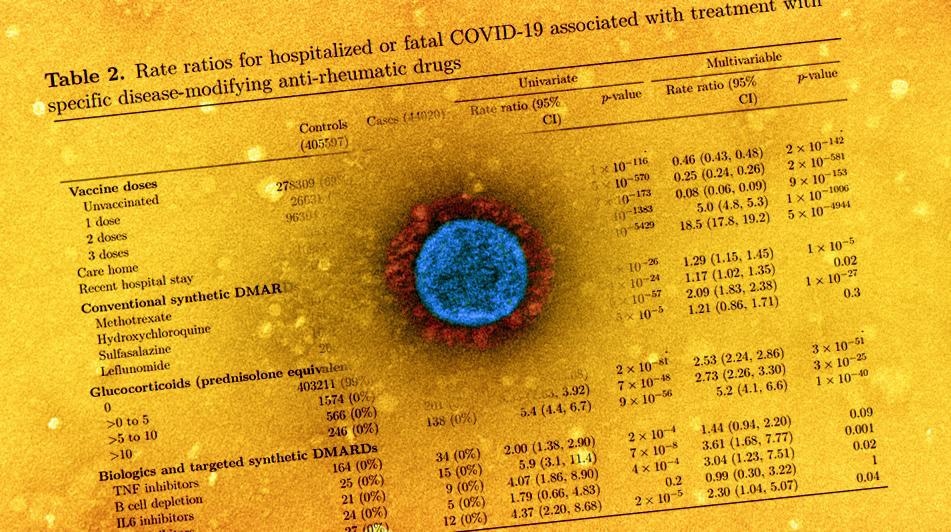
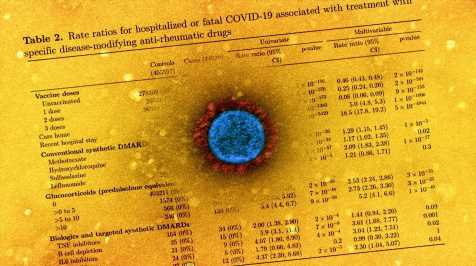
The central objective of the study was to assess hospitalization or a fatal outcome due to COVID-19. Patients of autoimmune rheumatic disease were stratified into three groups – rheumatoid arthritis, connective tissue disorders, and psoriatic or other seronegative arthropathies. Further, those who used conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs) like hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), methotrexate, prednisolone, in the last 240 days were screened.
Additionally, rheumatologic outpatient consultation data from the last five years was used as a proxy to exclude patients receiving csDMARDs for non-rheumatic disorders. Finally, rate ratios were calculated by conditional logistic regression for COVID-19-related hospitalizations or fatalities.
Findings
Around 4,633 individuals were identified with IRD in the merged biologics list. Of which, 2702 people had rheumatoid arthritis, 1,765 patients of psoriasis or other seronegative arthritis, and 141 individuals were diagnosed with connective tissue disorder. Among these, 433 people contracted SARS-CoV-2, with 58 of them requiring hospitalization within the first 14 days, seven cases under critical care within 21 days of COVID-19 diagnosis, and 14 patients succumbed to COVID-19 within 28 days of COVID-19 diagnosis.
Public Health Scotland (PHS) identified 2,527 out of 4,633 patients and categorized them for shielding (due to high vulnerability). From the biologics list, about 2,586 patients were sampled previously in the REACT-SCOT study, and almost everyone (2,583) had an outpatient rheumatology consultation in the last five years. Still, only 1,229 were on csDMARDs during the previous 240 days.
The rate ratio of IRD patients for hospitalized or fatal COVID-19 outcomes was 2.68 in rheumatoid arthritis patients, 3.27 for psoriatic or other seronegative arthritis cases, and 2.28 for connective tissue disorders. The rate ratio for severe COVID-19 patients associated with csDMARDs was 2.14, 2.01 for patients taking tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, and 3.83 for those receiving other biologics. The researchers noted that the highest rate ratio for IRD patients was those using B cell-depleting agents as DMARDs.
Conclusions
The authors observed that people on csDMARDs were twice as likely to have a hospitalized COVID-19 outcome than the general public. Notably, the IRD patients treated with glucocorticoids had a more significant risk of COVID-19 hospitalization. The use of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors and B cell depleting drugs was associated with increased COVID-19 risk than HCQ, methotrexate, and TNF inhibitors.
The comparison of the present findings to other studies revealed that the rate ratio (2.1) for rheumatology patients on csDMARDs hospitalized due to COVID-19 was higher than the rate ratio (1.3) for mortality associated with lupus or psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis. Patients taking TNF inhibitors and those using methotrexate were found to have a similar rate ratio for COVID-19 hospitalization.
Interestingly, some earlier studies reported the use of HCQ/sulfasalazine not to affect COVID-19 susceptibility, but the present study observed a higher rate ratio for COVID-19 hospitalization in HCQ- and sulfasalazine-prescribed patients, which was as high as methotrexate users. The authors proposed that the observed increase in risk could be attributed to the disease rather than the effects of immunosuppressive drugs.
*Important notice
medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information
- Risk of severe COVID-19 in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases treated with immunosuppressive therapy in Scotland, Paul M McKeigue, Duncan Porter, Rosemary J Hollick, Stuart J Ralston, David A McAllister, Helen M Colhoun, medRxiv, 2022.02.13.22270898, DOI: 10.1101/2022.02.13.22270898, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.02.13.22270898v1
Posted in: Medical Research News | Medical Condition News | Disease/Infection News
Tags: Arthritis, B Cell, Cell, Consultation, Coronavirus, Coronavirus Disease COVID-19, Critical Care, Drugs, Exercise, Hospital, Hydroxychloroquine, Kinase, Lupus, Methotrexate, Mortality, Necrosis, Primary Care, Psoriasis, Psoriatic, Public Health, Research, Respiratory, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Rheumatology, SARS, SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Syndrome, Tumor, Tumor Necrosis Factor

Written by
Tarun Sai Lomte
Tarun is a writer based in Hyderabad, India. He has a Master’s degree in Biotechnology from the University of Hyderabad and is enthusiastic about scientific research. He enjoys reading research papers and literature reviews and is passionate about writing.
Source: Read Full Article