Treating aggressive breast cancer with an anti-diabetic drug
National University of Singapore researchers developed an approach to target highly resistant triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs) by interfering with their energy production using cytotoxic gold-metformin prodrugs.
Metformin is a widely prescribed “over-the-counter” medication for Type 2 diabetes. There is some evidence that patients taking metformin for a long time have significantly reduced risk of developing cancer. However, despite well-characterized anticancer effects and the low cost of metformin, its use as an anticancer agent has serious drawbacks. Metformin is poorly taken up by cells. In order to achieve therapeutic concentrations, it has to be taken repeatedly in high doses, which may cause serious side effects in cancer patients.
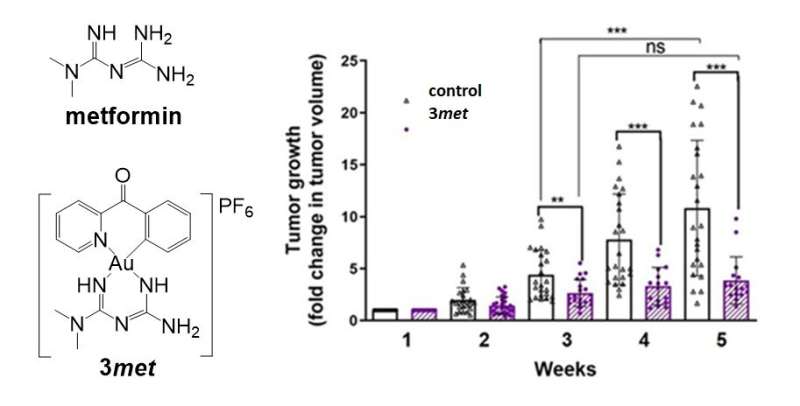
A team of researchers led by Prof Ang Wee Han from the Department of Chemistry, National University of Singapore and Prof Maria Babak from City University of Hong Kong devised an approach to chemically conjugate metformin, as well as its analog phenformin. This is achieved by using a gold-based active molecular fragment to improve bioavailability and to achieve synergistic action of the two key components (metformin and gold molecules). By taking advantage of the electrochemical activity of the gold-based molecule, the team successfully delivered metformin into cancer cells with high selectivity. The anticancer activity of the lead drug candidate developed by the team named 3met, was found to be more than 6,000 times higher when compared to metformin.
Prof Ang said, “TNBCs represent an especially dangerous subset of breast cancers with the poorest prognosis and limited treatment options. However, this particular aggressiveness of TNBC cells is related to their increased dependence on glucose and lipids, which provide additional energy to sustain rapid cancer growth. Since our drug candidates interfered with energy production in the cancer cells, we hypothesized that TNBCs might be particularly responsive to such treatment.”
Source: Read Full Article