Replacing microglia in mice using circulation-derived myeloid cells to treat neurodegenerative disease

An international team of researchers has developed a way to replace almost all of the microglia cells in a mouse brain using circulation-derived myeloid cells as a way to treat neurodegenerative disease using a technique that does not require genetic manipulation of either a host or donor. In their paper published in the journal Science Translational Medicine, the group describes their new technique and the improvements they saw in mice after treatment with the new procedure.
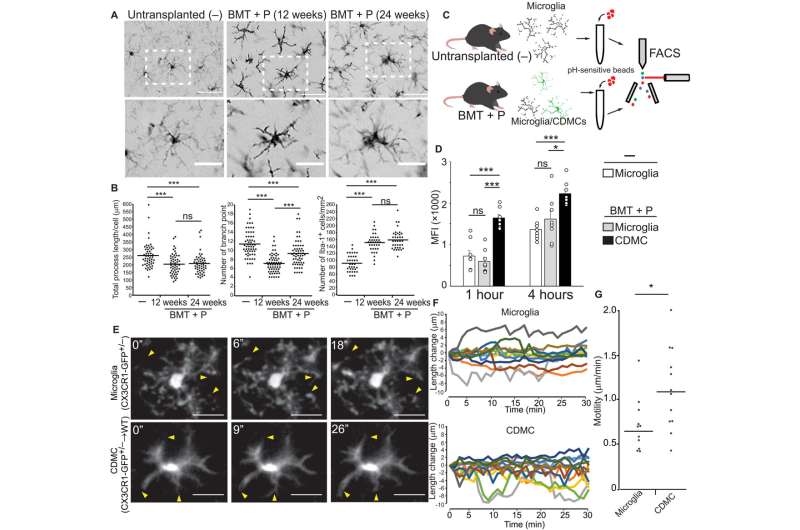
One of the ways doctors attempt to treat some neurodegenerative diseases is via cell therapies. But such an approach is often hindered by the difficulty in getting the cells to distribute themselves once transplanted into a patient. In this new effort, the researchers have found a way to replace a type of defective immune cell, known as microglia, with new ones.
Microglia exist in the brain—their job is to remove dead cells and to identify and clear defective proteins. Prior research has shown they play a role in memory formation and has also linked some kinds of neurogenerative diseases to defective microglia. In this new effort, the researchers sought to replace defective microglia in a mouse brain with microglia from other mice that were not defective. Their approach involved giving test mice a drug that killed the microglia in their brains and then replacing them with circulation-derived myeloid cells—such cells are able to incorporate themselves into the brain where they generate microglia-like cells.
Testing of the new approach with mice that had a neurodegenerative disease related to defective microglia (where they had lower than normal levels of prosaposin) showed the approach to be effective. Those mice that received the transplants had less brain inflammation, had a longer life and showed improvement in motor skills.
Source: Read Full Article