Hip Replacement: Get Acquainted with Procedure Peculiarities
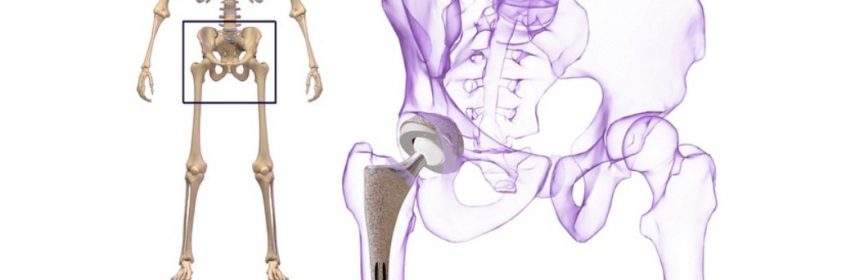
The hip joint can also be called as a hinged joint. The upper part of the movable femur joins the area of the pelvis (acetabulum). This connection allows the joint to move freely in different directions.
The British orthopedist John Charnley invented a hip prosthesis and developed the basic principles of surgery in the late ‘60s of the last century. This prosthesis is still used but due to the new materials, it can boast of high strength and durability, which made it possible to significantly extend the life of the endoprosthesis.
Reasons for hip replacement surgery
The most common causes of hip joint dysfunction are:
- Arthrosis.
- Arthritis.
- Consequences of improper bone fusion after a fracture.
- Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head.
- Bilateral fibrous or bone ankylosis.
- Transvertebral fractures in the persons of riper years, etc.
Which tests have to be done before hip surgery?
The patient must undergo several checking procedures before hip replacement in Germany. The physician prescribes determination of blood group and Rhesus factor, RW, clinical blood analysis, urine, biochemical blood assay, etc. It is necessary to do an MRI, radiography, or CT, as with their help the specialist more clearly examines the anatomical structures of the hip joint and its changes. If the patient has chronic diseases that may affect the operative or postoperative period, he/she has to consult with a cardiologist, endocrinologist, physician, vascular surgeon, etc.
Which prostheses can be proposed?
There are cement (endoprosthesis is attached with medical bone cement) and cementless implants (bone grows into the surface of the endoprosthesis) depending on the method of attachment. The recommended endoprosthesis with mechanical fixation (cementless) consists of titanium and cermets, so it guarantees high reliability and minimum wear. The cement-free implant doesn’t work against the MRI performing, as the specified unit is inert to the magnet. Cement arthroplasty is performed when replacing the knee joints and has minor indications during the hip joints replacement.
After the procedure
The status post person stays in the intensive care unit of a hospital (during 2-3 hours). The patient is given antibiotics, painkillers, and anticoagulants for another 2-3 days. Bandages are made with an elastic roller on both lower extremities in order to reduce venous blood stagnation in the patient’s legs. Complications are very rare after arthroplasty and the alarming signs are:
- Temperature rise.
- Redness of the skin in the postoperative wound.
- Sudden pain in the area of the operated joint.
- Swelling, numbness, or tingling in the leg on the prosthesis side.
- Discharge from the wound.
On the first day after hip replacement, the person is allowed to stay in bed in a sitting position, do exercises for the muscles, and respiratory maneuvers. Some patients can walk with the help of an instructor using crutches. The sutures disappear by themselves in 3 weeks (at home). It is necessary to follow all the recommendations of the surgeon after discharge from the hospital.