The role of perineural networks in disorders such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder
Juan Nácher, professor at the Department of Cell Biology at the University of Valencia, has conducted research on the role of perineuronal networks (PNN) in the adult brain and their incidence in psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder.
The study, published in the Journal of Neuroscience, could facilitate new diagnostic tools or treatments for these diseases.
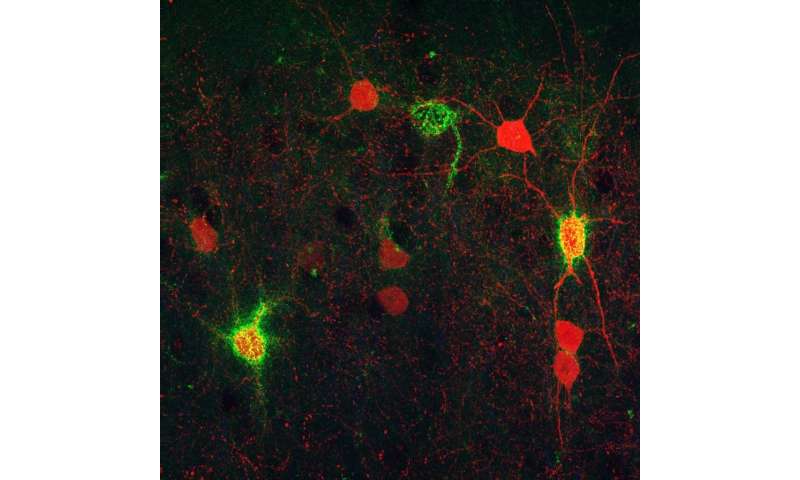
Inhibitory neurons that express parvalbumin (PV+) are crucial for the function of the prefrontal cortex and alterations have been found in these cells in different psychiatric disorders. The development and plasticity of the connectivity of these neurons is strongly regulated by specialized regions of the extracellular matrix (the molecules that occupy the spaces between neurons). These regions of the matrix are called perineural networks and particularly surround many PV+ neurons.
The team led by Juan Nácher has compared PV+ neurons with PNN or without PNN around. By digesting PNNs with a specific enzyme, the study revealed that these regions of the extracellular matrix markedly influence the connectivity and function of PV+ cells in the adult prefrontal cortex.
Specifically, the inhibitory connections received by these interneurons are particularly affected by the presence of PNN. The depletion of PNNs also affects the functioning of PV+ interneurons and alters gamma activity, a dependent oscillation of these cells.
The researchers studied the connectivity of PV+ neurons using immunohistochemistry and confocal microscopy. The synaptic connections these neurons receive and send have been analyzed by comparing cells surrounded and not surrounded by PNN, and also by analyzing the prefrontal cortex of animals that had PNN removed by a specific enzyme. Finally, the function of these cells was evaluated by studying the electrical brain rhythms in which they are involved.
Source: Read Full Article