Illuminating the brain with an ultra-thin, flexible, multipoint microLED array film
Researchers at Toyohashi University of Technology, Dokkyo Medical University and the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University have developed a flexible, multipoint microLED array film. The film can be flexibly attached to cover the brain and can illuminate specific regions of it as microLEDs are arranged along multiple points of it.
In recent years, optogenetics has enabled the manipulation of neural activity by light. While this technique requires a light-emitting device, there were no optical devices that could be attached to cover entire tissues such as the brain, with the light only influencing target neurons, or that could be implanted in an organism so that the activity would be freely manipulated by light.
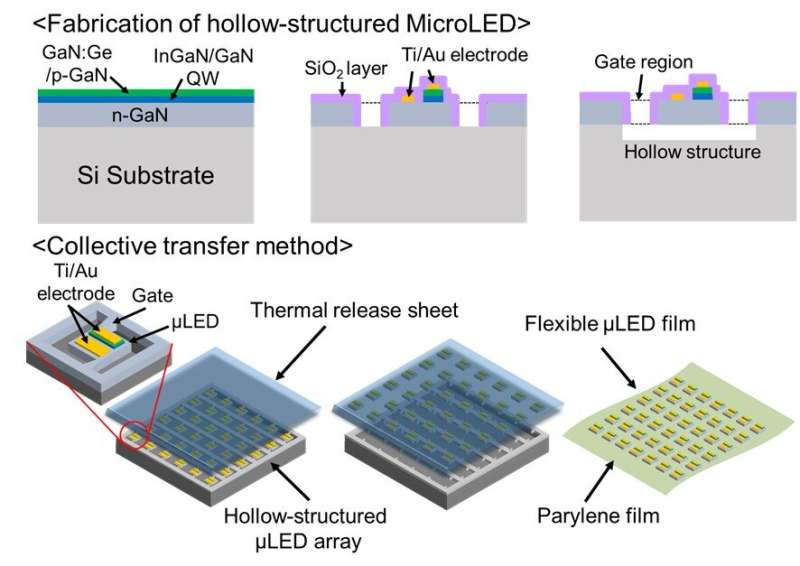
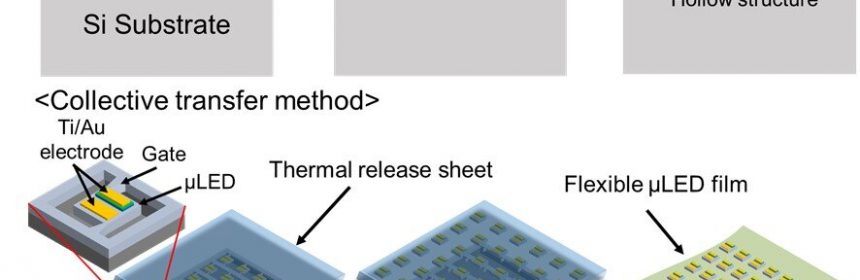
To implement this device, a thin, lightweight, and flexible body is required. It was thus necessary to establish a technology to arrange an LED layer a couple of micrometers thick highly precisely on an ultra-thin film that is not harmful or toxic to living tissue. The research group this time has established both (1) a technology to form a hollow structure of microLEDs with high density and in minute detail, and (2) a high-precision batch transfer technology using a thermal release sheet. With these technologies, it has also successfully developed an ultra-thin, lightweight multipoint microLED array film that maintains lighting performance even when the film is bent. The application of the developed device is expected to create a new area of neuroscience research aimed at comprehensively understanding the brain information that underpins how neural activity, behaviors, and disorders are linked.
Details
At present, attempts are being made to use light to manipulate the activity of various functional molecules inside an organism. In particular, optogenetics—a technique to activate neural activity with light by expressing photosensitive proteins that react to a specific color of light in neurons—has a high temporal resolution and has been utilized to elucidate brain function. However, to comprehensively elucidate the complex neural network created by neurons in the brain, it is necessary to employ light stimulation that will enable free manipulation of certain regions of neurons distributed across a wide range of the brain. The application of conventional optical fibers and microscopes is not sufficient to illuminate certain or multiple regions at the same time and also restricts the free movement of animals. Although this meant high hopes for the application of an implantable LED device, the size of commercial LEDs is as large as 200 µm with thickness of tens to one hundred micrometers, so that it cannot cover a wide range of the brain. As such, it was regarded as unsuitable as a device to stimulate specific neurons in the regions.
Given this, the research group sought to utilize a flexible film that is thin, lightweight, and bendable, and took the challenge of fabricating microscopic and ultra-thin microLEDs less than 100µm in size and a couple of micrometers in thickness and arranging them on multiple points. To achieve this, the group adopted the anisotropic wet etching method using potassium hydroxide to selectively remove the bottom LED layer, which led to the formation of a hollow structure of microLEDs that are arranged at high density. As the hollow structure separates the LED layer from the substrate, only the LED layer can be removed at one time using a thermal release sheet with no damage to either microLEDs or biocompatible Parylene films. By applying this technique, the group has successfully fabricated a microLED array on the film. This microLED-mounted film maintains the lighting performance even when being bent. It has also been verified that bright blue light can be obtained and used in actual optogenetic experiments with the film adhered to the surface of a mouse’s brain.
Future outlook
The multipoint microLED film developed through this study has potential broader application with the brain and will realize the control of complex brain activity freely in the spatiotemporal aspects. The brain has diverse functionalities in various regions and serves to manipulate the whole body in a complex way. By combining measuring technology in the future, the application of this technology is expected to create a new area of neuroscience research aimed at comprehensively understanding the brain information that underpins how neural activities, behaviors, and disorders are linked. Further, with the development of photosensitive functional molecules inside an organism, it is expected that it will be possible to illuminate light onto areas where medicine is targeted and make the medicine effective in any time, which will lead to the application of the phototherapy technology using devices implanted in organisms.
Source: Read Full Article