FOCUS may lower PE diagnosis in ED patients with suspected PE and abnormal vitals

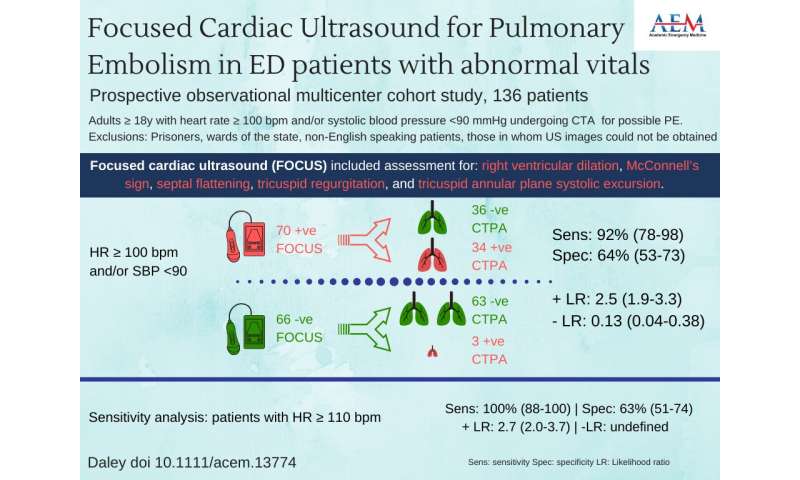
Focused cardiac ultrasound (FOCUS) performed by emergency physicians with advanced training in emergency ultrasound may significantly lower the likelihood of the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism (PE) in most patients who are suspected of PE and have abnormal vital signs. This was especially true in those patients with a heart rate > 110 beats/min. That is the conclusion of a study to be published in the November 2019 issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), a journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
The lead author of the prospective observational multicenter cohort study is James I. Daley MD, MS, MPH, an instructor in the Department of Emergency Medicine at Yale School of Medicine. Daley et. al suggest that further study in a larger cohort of patients (which would yield narrower 95% confidence intervals) is required before focused cardiac ultrasound can be used to reliably exclude pulmonary embolism in this patient population.
The results suggest that FOCUS can be an important tool in the initial evaluation of emergency department (ED) patients with suspected PE and abnormal vital signs.
Commenting on the study is Robert R. Ehrman, MD, MS, the director of emergency ultrasound research at Wayne State University School of Medicine/Detroit Medical Center in Detroit, MI:
Source: Read Full Article